 2
2
 2
2
IP address is an address having information about how to reach a specific host, especially outside the LAN. An IP address is a 32 bit unique address having an address space of 232. Generally, there are two notations in which IP address is written, dotted decimal notation and hexadecimal notation.
Classful Addressing
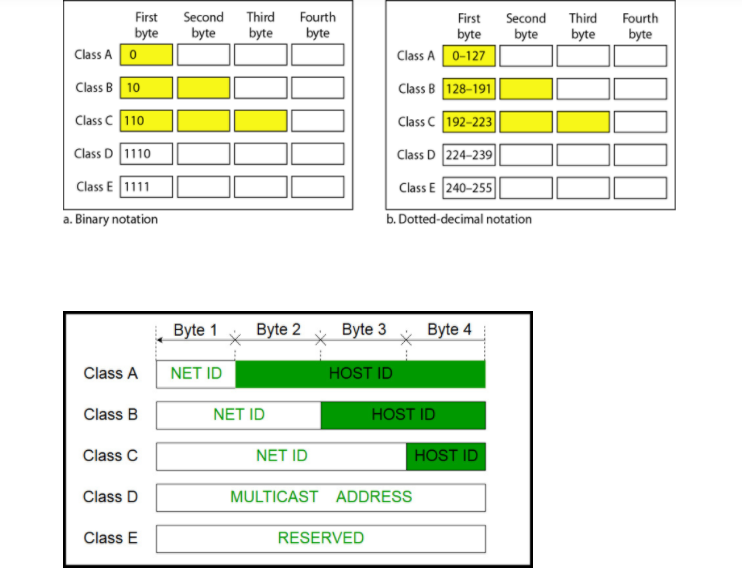
In Classful addressing, the address space is divided into five classes: A, B, C, D, and E. Each of these classes has a valid range of IP addresses. Classes D and E are reserved for multicast and experimental purposes respectively. The order of bits in the first octet determine the classes of IP address.
IPv4 address is divided into two parts:
- Network ID
- Host ID
The class of IP address is used to determine the bits used for network ID and host ID and the number of total networks and hosts possible in that particular class. Each ISP or network administrator assigns an IP address to each device that is connected to its network.
Note: While finding the total number of host IP addresses, 2 IP addresses are not counted and are, therefore, decreased from the total count because the first IP address of any network is the network number and whereas the last IP address is reserved for broadcast IP.
The Classful addressing wastes a large part of the address space.
- Class A: 0----2^7---- 2^24
- Class B: 10--- 2^14--- 2^16
- Class C: 110---- 2^21--- 2^8
- Class D: 1110---1------ 2^28
Problems with Classful Addressing:
The problem with this classful addressing method is that millions of class A address are wasted, many of the class B address are wasted, whereas, number of addresses available in class C is so small that it cannot cater the needs of organizations. Class D addresses are used for multicast routing and are therefore available as a single block only. Class E addresses are reserved.
Since there are these problems, Classful networking was replaced by Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) in 1993.
